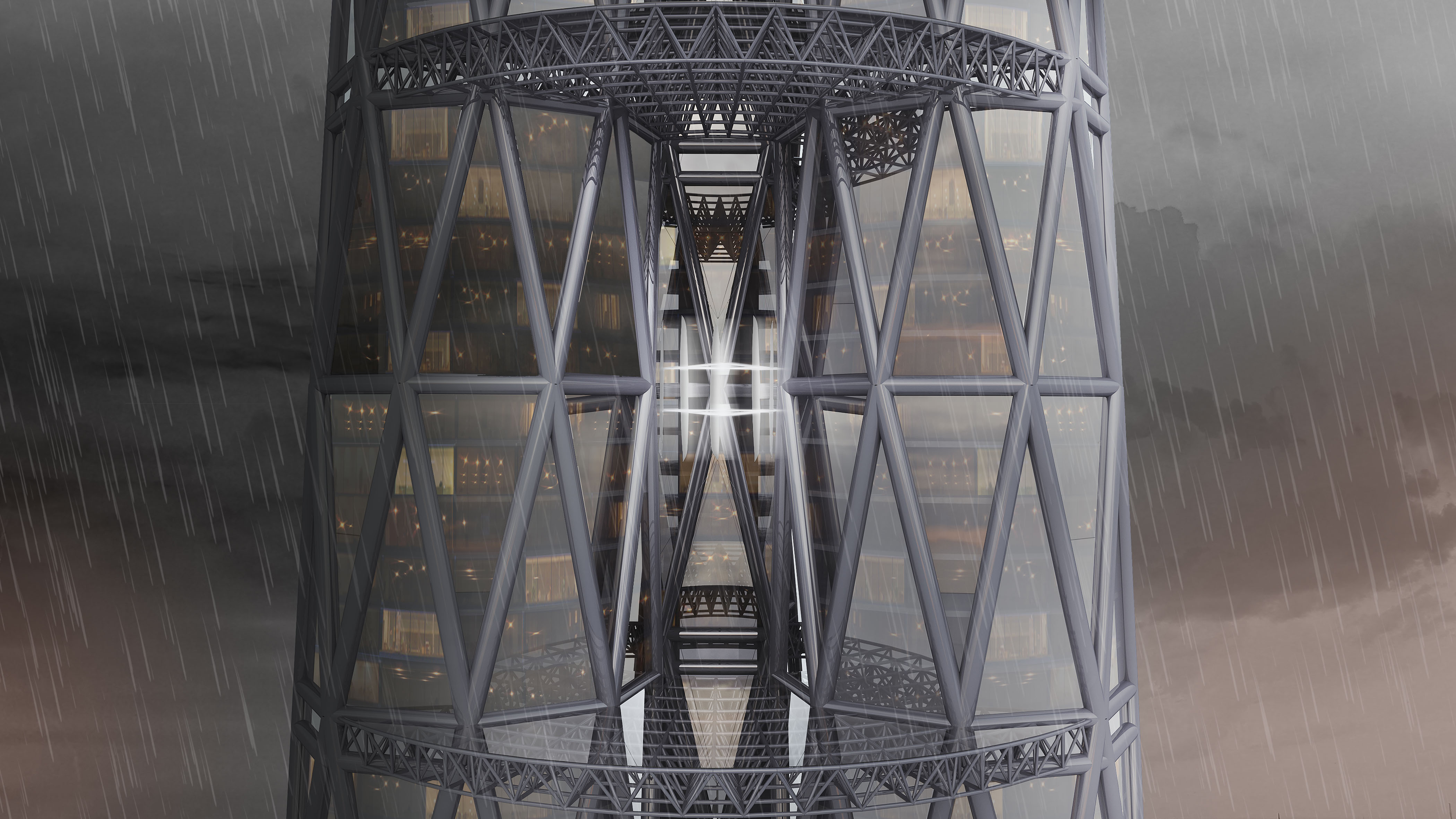
Morphogenesis of a bundled tall building: Biomimetic, structural, and wind-energy design of a multi-core-outrigger system combined with diagrid

Abstract
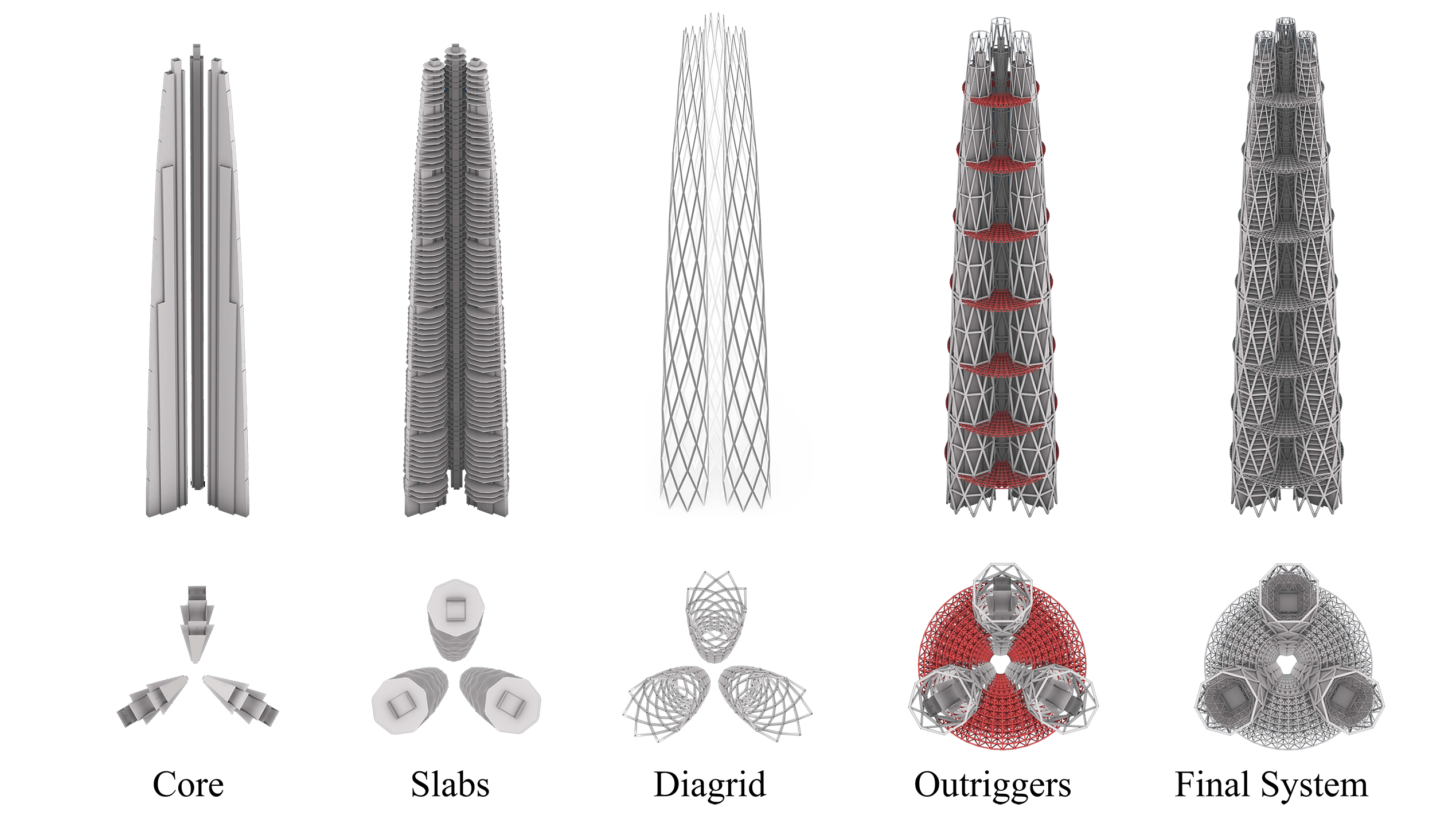
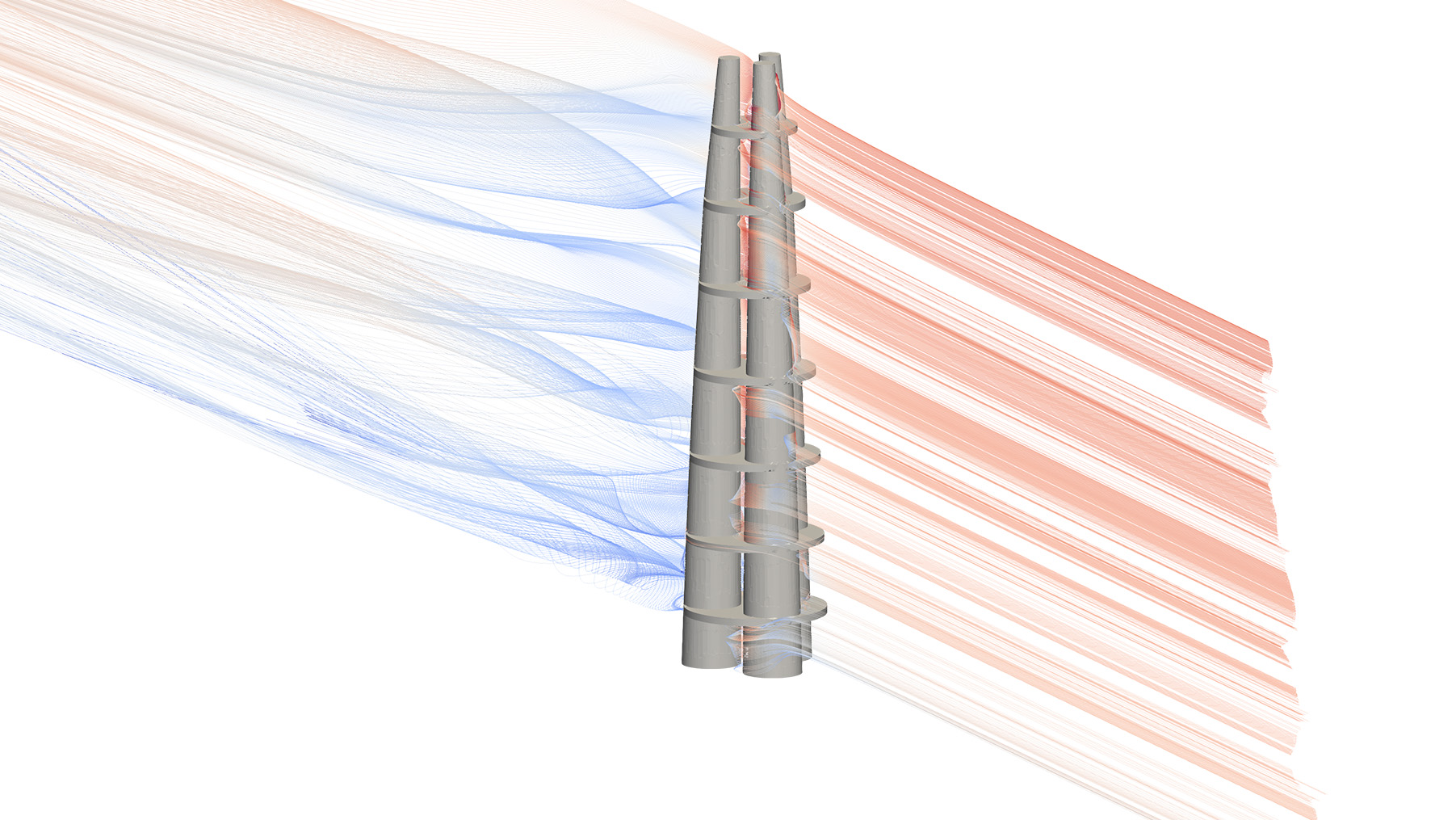
Skyscrapers are among the most distinctive building types of the modern age. Since many resources are attributed to these buildings, their design should consider a proper performance-based construction economy and environmental sustainable development. This research introduces a new concept for a bundled tall building founded on the use of a multi-core-outrigger system, which is additionally enriched with diagrid structures. The concept is inspired by the bamboo plant and follows the biomimetic design principles for the structural organization and performance-based criteria for optimizing the lateral stiffness and for shaping the cross section. Particularly, the incident wind speed is maximized to exploit Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs), which are located along the whole building height at the center of the bundled towers. The building morphogenesis is accomplished by a multistep methodology that is fully developed in a parametric environment and includes structural and computational fluid dynamic analyses. With the aim of validating the proposed concept, a case study of a 320-m-tall three-core building has been designed for the city of Pisa, Italy. The use of VAWTs results in an annual emissions reduction of about 10 kgCO_2/m^2. https://doi.org/10.1002/tal.1839