Architectural Geometry
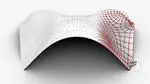
The development of computational tools and manufacturing techniques is continuously pushing forward the limit of feasible shapes in architecture. Along with new creative freeforms, new issues arise on structural design, economic sustainability and, more generally, on architectural style. These challenges ask for a new approach to architectural design where form is driven by statics, manufacturing, material compliance, and other aspects which have implications on construction and cost, but are not disruptive to the creative aim.
Architectural Geometry (AG) is an interdisciplinary research field born around 2007 to tackle some of the problems arising in the design of freeform structures. AG has its roots in classical and discrete differential geometry, and draws from different disciplines such as geometry processing, computer-aided design, structural engineering, and optimization. The main goal of AG is to find theoretical insights to develop computational design tools that can assist architects towards a smart design of freeform shapes which is aware of the essential constraints in the architectural application (structural behavior, fabrication issues, material availability, cost limitations). Here at the VCLab we have been pursuing these objectives for almost 10 years starting to tackle these problems from large scale digital fabrication.
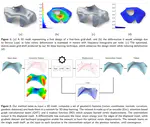
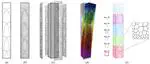
Until now, the main ingredients in architectural geometry have been discrete differential geometry and numerical optimization: the potential of artificial intelligence has been explored only to a lesser degree. At the VCLab, we have started investigating deep learning architectures that consume geometric data representing gridshells, and yield optimized, statics-aware structures.
Moreover, in the last decades new research lines have started developing in AG with the objectives to meet sustainable development goals. So architectural structures are required to pursue lightness, material-efficiency and fabrication economy. As a counterpart, they systematically increase the engineering design challenges related to the material behavior, the global mechanical performance and technical feasibility.